Introduction:
Embarking on your journey into the digital realm, understanding URL parameters is akin to acquiring a compass for navigating the vast landscape of the internet.
These seemingly enigmatic strings of characters appended to web addresses hold the key to unlocking profound insights into website functionality and optimization. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll unravel the mysteries surrounding URL parameters, exploring how they work, their various types, and their significance for marketers and SEO practitioners.

By delving into best practices and addressing potential pitfalls, you’ll emerge equipped to harness the power of URL parameters to elevate your online presence and drive success in the digital arena.
How Do URL Parameters Work?
URL parameters serve as directives to web servers, instructing them on how to dynamically generate and display content. When appended to a URL, these parameters communicate specific instructions to the server, such as filtering content, tracking user interactions, or customizing page displays based on user preferences.

For example, in an e-commerce website, URL parameters might specify the desired product category, sorting options, or price range, enabling users to tailor their browsing experience.
Types of URL Parameters:
URL parameters can take various forms, each serving distinct purposes in influencing website functionality and user experience. Common types include:

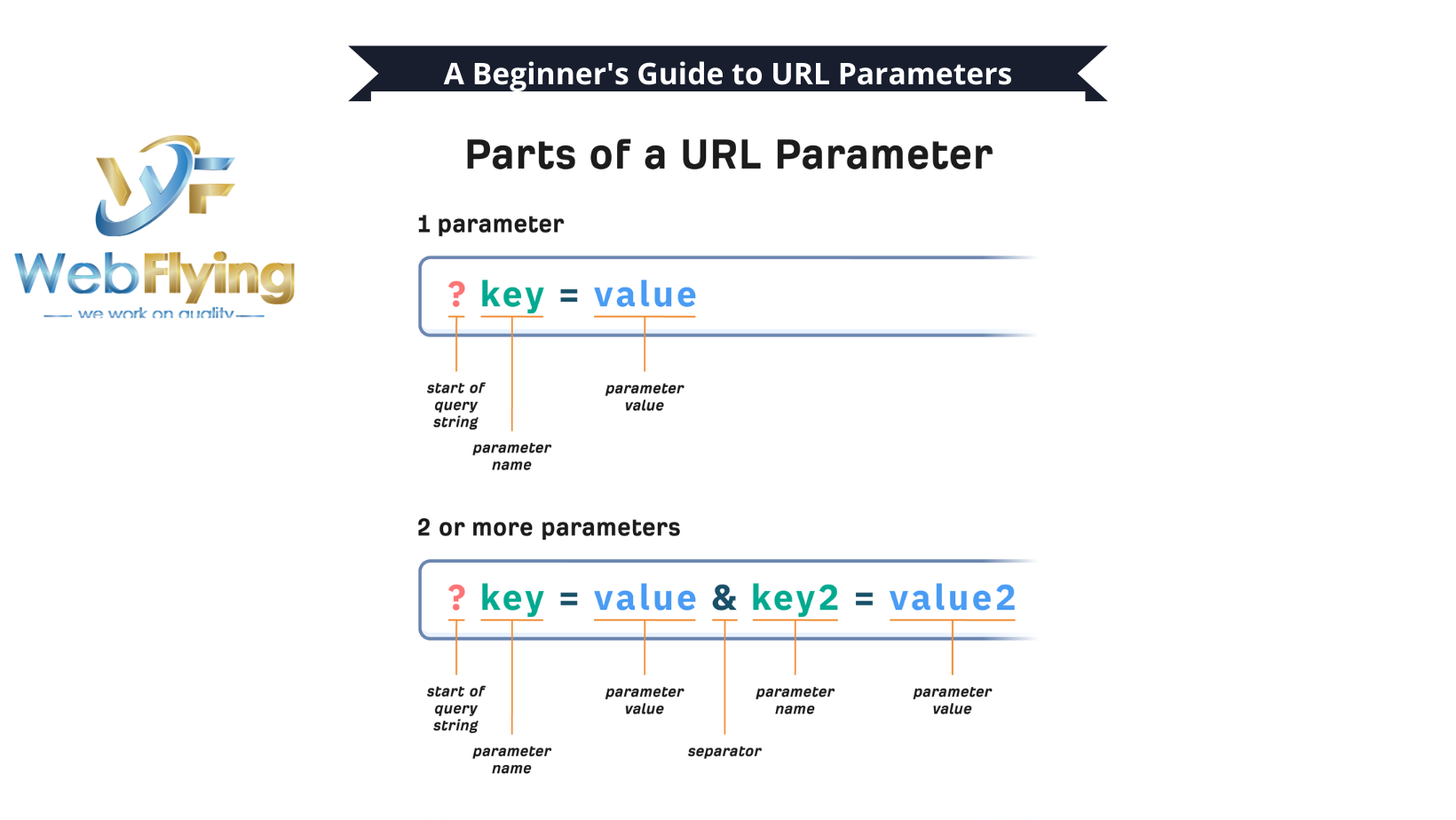
- Query Parameters: These parameters appear after the “?” in a URL and typically consist of key-value pairs separated by “&”. They are commonly used for filtering or sorting content, as seen in search engine queries or e-commerce product listings.
- Fragment Identifiers: Also known as anchors, fragment identifiers appear after the “#” in a URL and point to specific sections within a webpage. They facilitate seamless navigation to relevant content, particularly in lengthy articles or multi-page documents.
- Session IDs: Session IDs are unique identifiers appended to URLs to track user sessions and maintain stateful interactions between the user and the web server. They are often employed in e-commerce platforms or web applications to preserve user preferences across multiple page visits.
Why Are URL Parameters Important for Marketers?
URL parameters play a pivotal role in digital marketing strategies, offering marketers invaluable tools for tracking user behavior, personalizing content, and optimizing website performance. By leveraging URL parameters effectively, marketers can:

- Track Campaign Performance: URL parameters enable marketers to monitor the effectiveness of marketing campaigns by attributing website traffic and conversions to specific promotional channels or advertisements.
- Personalize User Experience: By dynamically generating URLs with tailored parameters, marketers can deliver personalized content to users based on their preferences, demographics, or past interactions.
- Improve Analytics Accuracy: URL parameters facilitate accurate tracking and analysis of website traffic, allowing marketers to gain insights into user engagement, conversion rates, and other key performance metrics.
How Google Deals with URL Parameters:
Google’s search engine crawlers are adept at handling URL parameters and understanding their impact on website content and indexing. To ensure optimal crawling and indexing efficiency, Google employs various techniques to process URL parameters, including:

- Parameter Handling Tools: Google Search Console provides webmasters with tools for managing URL parameters, allowing them to specify how Googlebot should treat specific parameters in terms of crawling and indexing.
- Canonicalization: Google utilizes canonical tags to consolidate duplicate content variations generated by URL parameters, thereby preventing indexing issues and preserving the integrity of search results.
- URL Parameter Configuration: Webmasters can configure URL parameters in their robots.txt file or utilize the “no index” meta tag to prevent Googlebot from crawling and indexing pages with irrelevant or duplicate content generated by parameters.
When Do URL Parameters Become an SEO Issue?
While URL parameters offer valuable functionality for enhancing user experience and website functionality, they can also pose challenges from an SEO perspective if mismanaged. URL parameters may become an SEO issue under the following circumstances:
- Duplicate Content: When URL parameters generate multiple variations of the same content, it can dilute the relevance and authority of the original page, leading to potential duplicate content issues and suboptimal search engine rankings.
- Crawl Budget Waste: Excessive URL parameters or poorly configured parameter handling can consume valuable crawl budgets, causing search engine crawlers to spend disproportionate time crawling irrelevant or low-value pages instead of focusing on indexing critical content.
- Index Bloat: Uncontrolled proliferation of URL parameter combinations may result in index bloat, where search engines index an excessive number of pages with minor variations, leading to inefficient use of crawl resources and potential ranking dilution.
Best Practices for URL Parameters:
To mitigate potential SEO issues and maximize the benefits of URL parameters, adhering to best practices is essential:

- Parameter Consolidation: Consolidate URL parameters by using canonical tags or URL rewriting techniques to canonicalize parameterized URLs to their preferred canonical versions, thereby consolidating link equity and avoiding index fragmentation.
- Parameter Handling Configuration: Utilize Google Search Console’s URL Parameter Tool to specify how Googlebot should handle specific parameters, such as crawling, indexing, or ignoring them altogether, based on their relevance and impact on content.
- URL Parameter Clean-Up: Identify and remove unnecessary or irrelevant URL parameters from internal links, sitemaps, and canonical tags to streamline website architecture and prevent index bloat.
- Monitor Performance Metrics: Regularly monitor key performance metrics, such as crawl rates, indexation status, and organic search traffic, to identify any anomalies or issues stemming from URL parameters and take corrective action promptly.
Are URL Parameters Harming Your Website’s Rankings?
While URL parameters can pose challenges from an SEO perspective, they are not inherently detrimental to website rankings if managed effectively.

By implementing proper parameter handling strategies, monitoring performance metrics, and adhering to SEO best practices, webmasters can mitigate potential issues associated with URL parameters and ensure their website remains optimized for search engine visibility and user experience.
Conclusion:
URL parameters are a double-edged sword in the realm of digital marketing and SEO, offering valuable functionality for enhancing user experience and tracking user behavior while posing challenges in terms of duplicate content, crawl efficiency, and indexation issues.
By understanding how URL parameters work, the various types, and their significance for marketers and SEO practitioners, you can harness their power to optimize website performance, drive targeted traffic, and elevate your online presence effectively.
Armed with the insights and best practices outlined in this guide, you’re well-equipped to navigate the complexities of URL parameters and steer your digital endeavors toward success in the ever-evolving landscape of the internet.